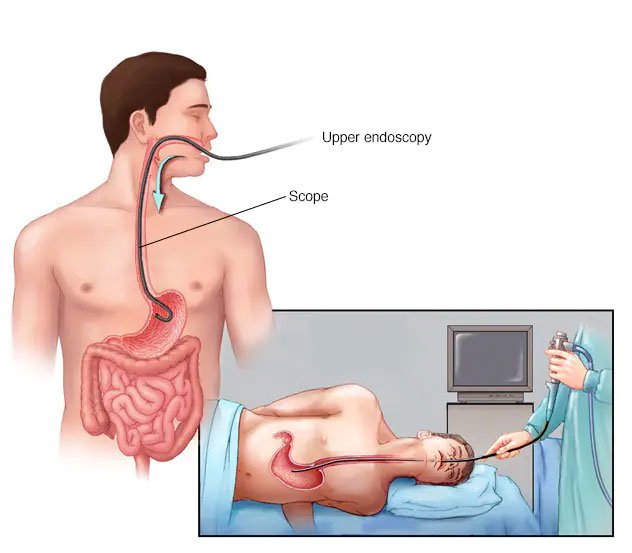
This procedure involves a gentle visual examination of the upper digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum), using a thin, flexible tube with a camera. It helps in diagnosing various conditions like ulcers, inflammation, and tumors, and allows for therapeutic interventions such as biopsies, polyp removal, and treatment of bleeding.
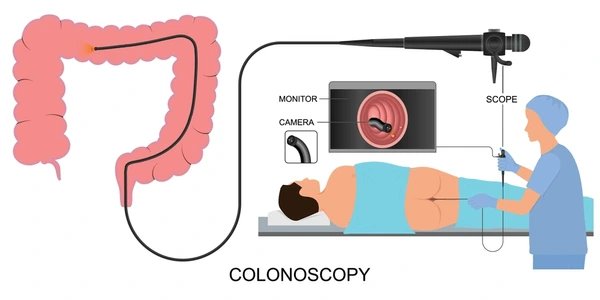
A comprehensive visual examination of the entire colon and rectum is performed using a flexible, lighted scope. This crucial procedure aids in the early detection of colorectal cancer, polyps, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Colonoscopy also enables therapeutic interventions like polyp removal and tissue sampling for diagnosis.
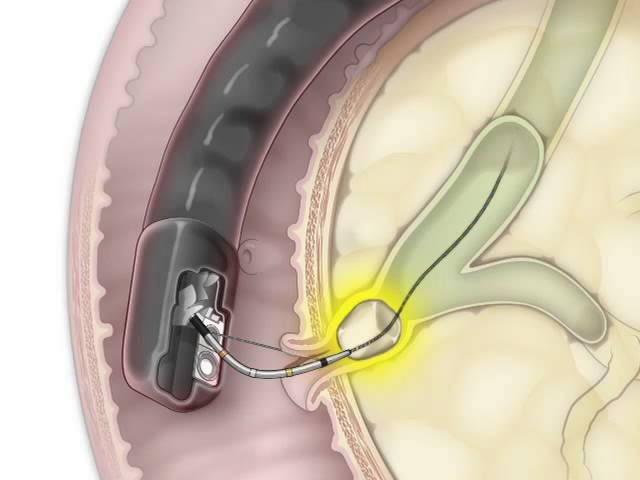
This advanced endoscopic technique is used to diagnose and treat problems within the bile and pancreatic ducts. It involves using an endoscope and specialized instruments to visualize the ducts, remove gallstones, relieve blockages, and obtain tissue samples when necessary.
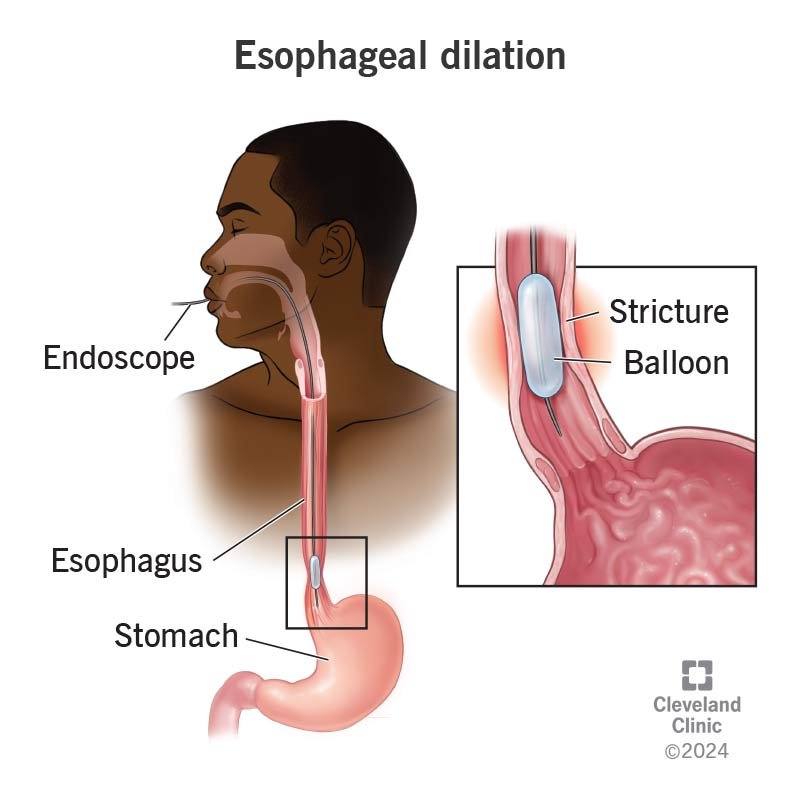
This therapeutic procedure is performed to widen narrowed areas (strictures) within the esophagus, which can cause difficulty swallowing. Various techniques, including balloons or dilators, are used to gently stretch the esophagus, improving the passage of food and liquids.
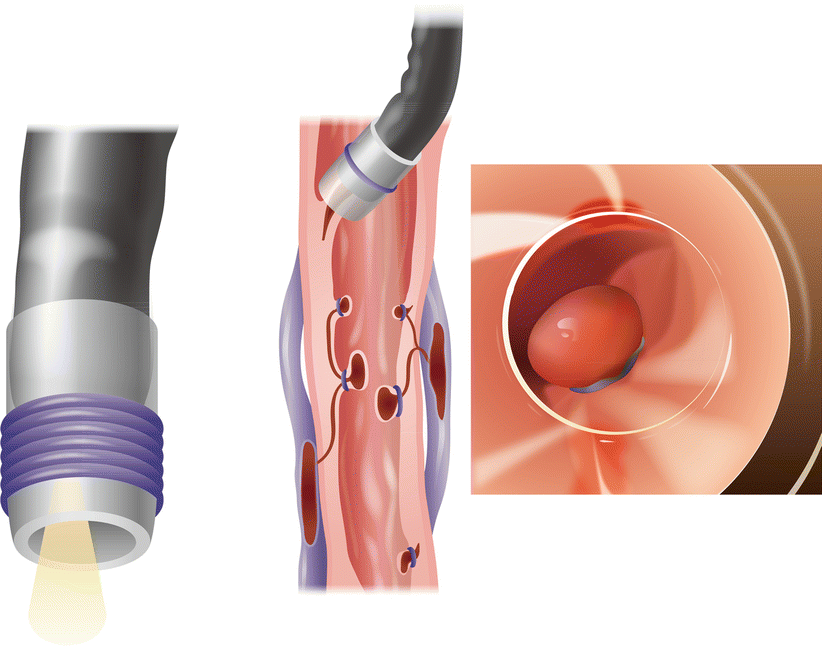
A specialized endoscopic treatment for bleeding esophageal varices, which are swollen blood vessels in the esophagus often caused by liver disease. EVL involves placing elastic bands around the varices to stop the bleeding and prevent future episodes.
When objects are accidentally swallowed and become lodged in the upper digestive tract, safe endoscopic retrieval is often the preferred method. Using specialized instruments passed through the endoscope, the foreign body can be carefully grasped and removed, avoiding more invasive surgical procedures.
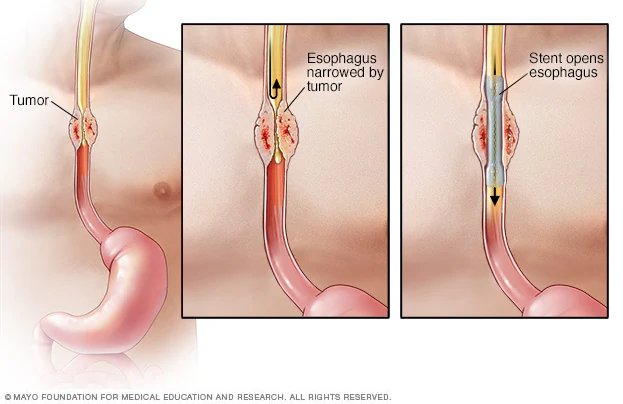
This procedure involves the placement of expandable metal tubes (stents) to open up and maintain the patency of blocked or narrowed areas in the esophagus, bile ducts, or intestines. Stenting can relieve symptoms like difficulty swallowing, jaundice, and abdominal obstruction, improving the patient's quality of life.